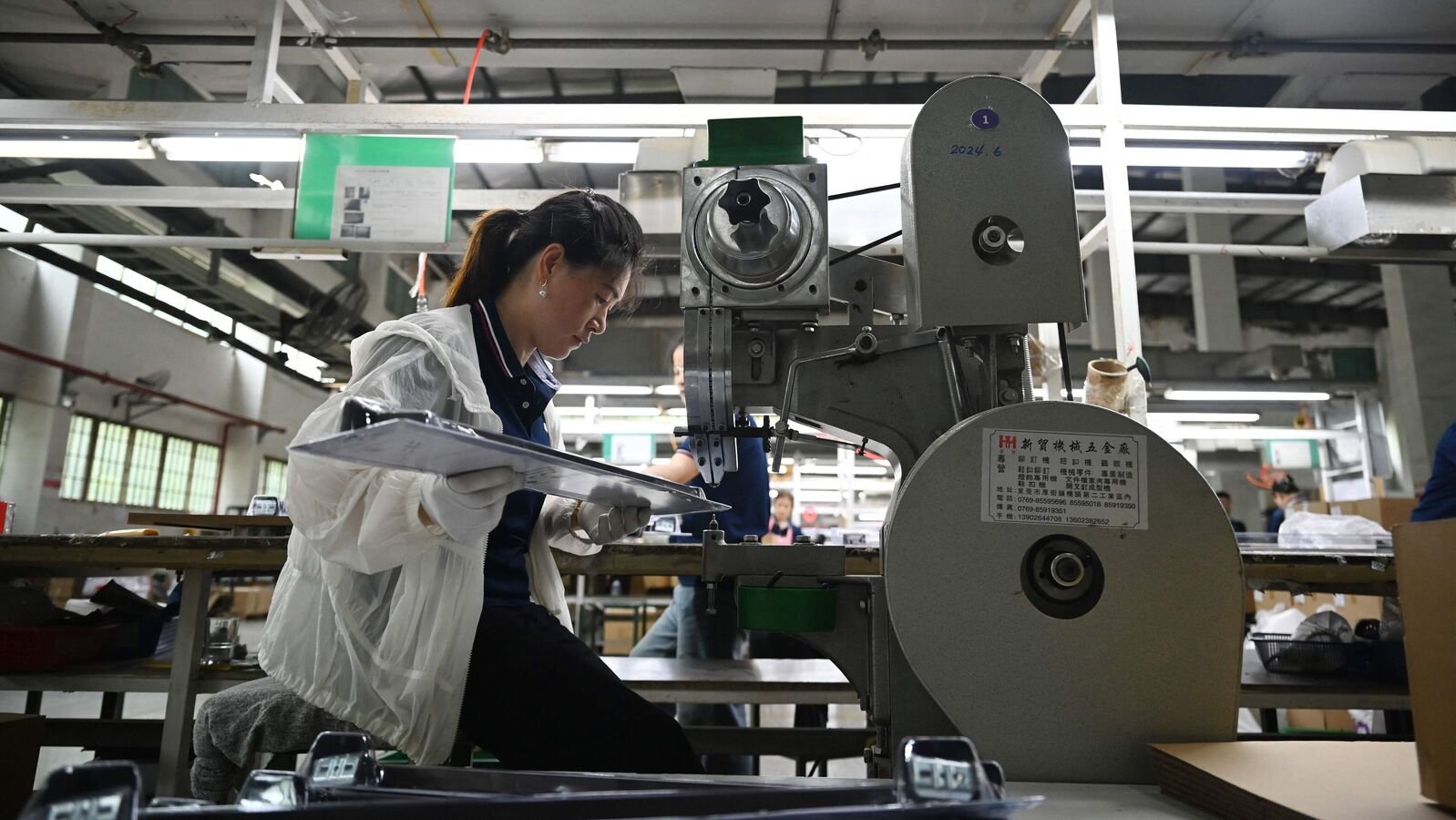
Despite the disruption of trade, slow domestic consumption, the persistent crisis of the real estate sector and the threat of deflation, the Chinese economy has managed adequate growth. MINT examines the sustainability of this growth and measures that China may take to appear unscathed.
How is the Chinese economy?
Despite the disruption of the trade caused by the US trade war, which briefly saw that Washington stored the tariffs that are in an incredible three digits, Chinese exports of goods remained robust. In the first five months of 2025, they increased by 6%. This, regardless of the 35% decrease in exports in May to the US – is the largest market. Home demand is also good. The retail sale in the first four months of 2025 increased by 4.8%, which is 1.5 percentage point better than in the same period last year. The Index of the May Purchase Manager, which was issued on Monday, showed a marginal improvement in production activity.
How did China manage this show?
The export has increased by focusing on markets outside the US. Exports to India, Brazil, East Asia and Europe increased sharply. The Chinese government also announced fiscal and monetary stimulus of 1.6% of its GDP in an effort to catalyze domestic demand. This includes subsidies for trading in consumer goods and cuts in housing loans. The consumption of household appliances and furniture showed two -digit growth in the first four months of this year’s growth. Public expenses have also increased. This caused the investment in infrastructure to increase by 11.6% in April compared to 10% last year.
Was the Chinese outlook for growth?
Citigroup increased the Chinese growth estimate to 2025 to 5% of previous 4.2%. According to the World Bank China in 2024 showed a growth of 5%. In the first quarter of 2025, its economy increased by 5.4%. That was before the new trade war. The World Bank projects a growth of 4.5% per 2025. If the Chinese economic show is maintained, there may be a revision of ascending.
What are the risk factors?
There are many. Although the US and China have concluded a business agreement, it remains fragile. Many countries increase their defense against cheap Chinese goods. This could damage exports. The revival of domestic demand is not based on a wide, reflecting weak confidence of consumer. Experts attribute this to slower income growth and uncertain job prospects. The crisis of the property sector looks sticky because the prices of houses continue to fall. Deflationary pressures remain. Experts say that the economy needs more stimuli.
What can Beijing do to improve things?
In addition to the initiative, economists demanded reforms that would solve the slowdown of productivity, high debt and aging populations that reduce economic growth. With little protection against health care and frayed social security network, the Chinese are retaining expenses when uncertainty increases. To improve the household expenditure, fiscal sources should be directed to improve medical coverage and safety network. The real estate crisis needs a permanent solution because falling house prices are damaging consumers’ sentiment.
(tagstotranslate) trade disruptions