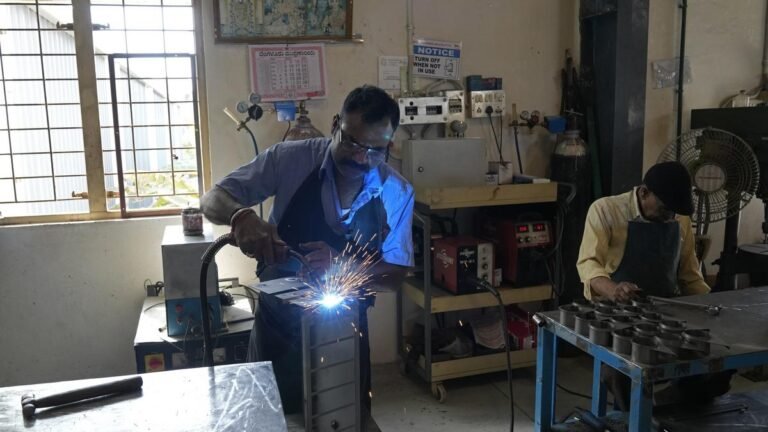
There are concerns that unrestrained radiation of forests will reduce the wilderness habitat and escalate the conflicts of human animals in the carnat. | Photo Credit: Ma Sriram
Karnataka has 44,812 cases of penetration into the forest on March 31, 2025, of which 559 fresh cases were registered during 2024-25, as evident to the eroding of forest cover and fragmentation of habitats.
The annual report of the Ministry of the Forest Department of Karnataka for 2024-25 also points out that out of 44,812 waiting cases, the number of interventions cleaned during the year was only 243, which underlines the low pace of recovery and impressive challenges in obtaining forests, despite growing environmental pressures.
The protectors claim that it would take decades to clean the existing pending items in which much of the degraded forest could irreversibly get lost. There are concerns that penetration cases that must be solved so far, and the number of fresh cases registered annually, is a sign that it is omitted at the ground level and lack of political support for eviction.
The affection is spreading through state reserve forests in all forest circles and divisions, and activists warned that the continuing occupation of forest origin limits the movement of wild animals and increases the conflict of human and tistin.
It is worrying is that some of the announced tiger reserves and sanctuary of wild animals also have promotion cases waiting for decades, of which 204 are in the Bandipur division, 16 in Nagarahole, 636 in the Bhanda division, 833 in the 709 division, Divisions, in a calive tiger division, in the division in the Kaliser division, in the division in Kalia in the Tiger division, in the division in the Kaliser division, in division 709 in the division in Kalise, division 709 in the division of Bhadra. Dandeli, among other things.
Of the 559 fresh cases registered during 2024-25, up to 38 cases were registered in the Shivamooga division, 53 in the Bhadravati division, 69 in Sagara and 24 in the Shivamogg Wildlife Division, while 7 fresh encroachment cases were registered in the Bidar division. Eshwar B. Khandre. Kanar Circle announced 69 new cases, while Belagavi (49), Chikkamagalur (41) and Kalaburgi (80) are other circles with a high number of fresh interventions.
Discharged cases of penetration, especially near the zones of wild animals, such as Bandipur-Nagarahole-MM Hills, have increased the alarm because these are sensitive areas where there were cases of conflict with human animal.
At a time when the wildlife population shows trends in growth, the inability to remove the intervention will disrupt and reduce the habitat and corridor of wild animals, forcing animals to get lost in villages adjacent to forests, increasing the conflict situation. By the way, the loss of human life due to conflict is also high in such regions as in Mysur, Kodag, Hassan, Chamarajanagar, etc.
According to the Ministry of the Environment, forests and climate change should be monitoring committees at the district level and on the basis of reviewing the situation on two -capacity and clearing eviction. Communication states that, in addition to monitoring forests, it should also remedy responsibility for officials, including income departments, for failing to prevent or avoid interventions. But due to the scope of interventions, activists are interested in whether the monitoring committees have become extinct.
Published – August 8, 2025 20:27